Screening

Filtration
– Physical and chemical processes – sedimentation, coagulation
– Membrane cleaning methods – ultrafiltration
The process of settling and clarification of water with the use of thin-film modules and recycle sludge to create the contact sludge
• Excellent quality of clarified water
• Lower doses of reagents
• Low space requirements
• Reliable technology, backed by a large number of completed projects
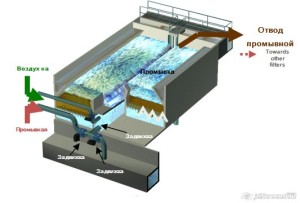
Upcoming free-flow filters
• The filter material with the same grit
– Reducing the height of filtered water over the surface of the sand (1.00 m)
– Pressure loss in order to avoid the possibility of contamination of the filter layer, caused by increased release of air from the water
- The hydraulic control system for each filter section
– Constant flow of water at the outlet of the filter due to the compensation of pressure losses that occur due to delay pollution
- Tangential flushing with raw water
– Effective removal of contaminants from the source water use
– Reducing the volume of waste water + energy

Fig. The membrane separation
Ultrafiltration – Continuous process
• Punching through a porous membrane
• Removal of suspended solids, organic matter and microorganisms
• Types: a dead-end filtration and tangential

Desalination:
• Filtration
• scavenger
• Ion exchange filters

– Counterflow
– Floating loading,
– Packed bed, air-flow,
– UFO / UPCORE
- Mixed
– Working, polishing, multistage
- Membrane Technology
- Reverse osmosis,
- EDI
- Ion exchange system with internal regeneration
– The efficiency of the separation and regeneration of the resins depends on
the ratio of the diameter of the filter to the height of the resin bed
– The sodium content (Na) £ 2 ppb
- External Regeneration
- – A few (1 to 4 pcs.) Of the individual filters, designed for the most efficient possible separation and regeneration of the resins
1 ppb£- The content of sodium (Na)
– Prevent possible penetration of the reagents used in the regeneration, in the condensate path through the use of additional filters regeneration
– Equipment for the regeneration and storage of reagents mounted in a room; the boiler room is not exposed to any hazards
- – A few (1 to 4 pcs.) Of the individual filters, designed for the most efficient possible separation and regeneration of the resins
Reverse Osmosis – Continuous technology
• The process of membrane separation
• The push by pressure through a semipermeable membrane
• Removal of salts, organic matter and microorganisms
• Type: tangential filtration
Electrodeionisation — EDI – RFIC technology – Continuous operation
• High quality treated water
• Small space requirements
• Minimum costs for automation
• Lack of wastewater contaminated reagents
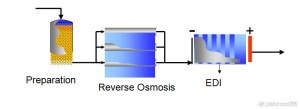
– Cation exchangerCondensate’s cleaning
• Carbon filters
• Anthracite filters
• Cartridge filters
• Ion exchange
– FSD anion exchanger with internal and external regeneration
– Filter ion exchange technology Multi-step exchanger
– Air-conditioning systems using reagents
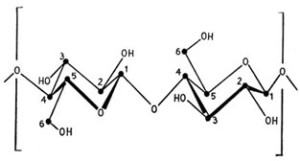
The structure of Cellulose – Filter
